Welding Engineering (IWE) and Inspection Service in Turkiye-Turkey
Ensure Weld Quality with QCmatic’s Expert Welding Engineering Services
Welding Engineering (IWE) and Inspection Service
QCmatic offers comprehensive third-party services encompassing welding engineering, visual testing, and documentation control to ensure the highest standards of welding quality and compliance. Our experienced team of welding engineers, inspectors, and documentation specialists collaborates closely with clients to deliver tailored solutions that optimize welding processes, detect defects, and maintain meticulous documentation throughout the welding project lifecycle.
Welding Engineering Services
QCmatic offers comprehensive third-party welding engineering services to support your welding operations and ensure compliance with industry standards and best practices. Our team of experienced welding engineers provides expert guidance and assistance at every stage of your welding projects, from planning and design to execution and inspection. Whether you need assistance with procedure development, welder qualification, or troubleshooting welding issues, we are here to help you achieve optimal welding performance and quality.
Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) Development
Our welding engineers work closely with your team to develop customized Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) tailored to your specific welding requirements and materials. We consider factors such as material type, thickness, joint design, welding process, and code compliance to create WPSs that ensure consistent and reliable weld quality.
Welder Qualification Assistance
We provide guidance and support for welder qualification testing to ensure that your welding personnel are properly qualified to perform the required welding tasks. Our welding engineers assist with test preparation, procedure review, and documentation to ensure compliance with industry standards and specifications.
Welding Process Optimization
Our welding engineers analyze your welding processes to identify opportunities for optimization and improvement. By evaluating factors such as welding parameters, equipment setup, and material selection, we help you enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve weld quality.
Welding Troubleshooting and Failure Analysis
In the event of welding issues or failures, our experienced welding engineers conduct thorough investigations to identify the root causes and develop effective solutions. Whether you are dealing with weld defects, cracking, or other issues, we offer expert analysis and recommendations to resolve the problem and prevent recurrence.
Welding Training and Education
We provide customized training programs and educational workshops to enhance the skills and knowledge of your welding personnel. Our training sessions cover topics such as welding fundamentals, process-specific techniques, safety practices, and quality assurance principles to ensure that your team is well-equipped to perform their welding tasks effectively.

Case Studies: Solving Welding Challenges with QCmatic’s Expertise
Problem: A client encountered weld distortion issues in large structural components fabricated by their Turkish supplier, leading to assembly difficulties and dimensional inaccuracies.
- Solution: QCmatic conducted a thorough analysis of the welding processes and parameters used by the supplier, identifying factors contributing to weld distortion, such as excessive heat input and inadequate fixturing. We collaborated with the supplier to implement corrective measures, including optimizing welding parameters, implementing preheating techniques, and redesigning fixturing methods. As a result, the client experienced reduced weld distortion and improved dimensional accuracy in their fabricated components.
Problem: A customer faced difficulties in achieving weld soundness and integrity in high-strength steel components sourced from Turkey, resulting in weld cracking and brittleness issues.
- Solution: QCmatic conducted a comprehensive review of the welding procedures and material selection criteria employed by the supplier, identifying deficiencies in heat treatment practices and filler metal selection. We worked closely with the supplier to develop revised welding procedures tailored to the specific material properties and project requirements. Additionally, we implemented stringent post-weld heat treatment protocols and conducted extensive quality testing to ensure weld soundness and integrity. As a result, the client achieved improved weld performance and reduced instances of cracking and brittleness.
Problem: A client faced challenges in meeting regulatory compliance and certification requirements for welded components sourced from multiple suppliers in Turkey, leading to delays in product launch and market acceptance.
- Solution: QCmatic conducted a comprehensive audit of the welding processes and documentation practices of each supplier, identifying gaps in compliance with regulatory standards and certification requirements. We worked closely with the suppliers to implement corrective actions, including updating welding procedures, enhancing documentation control systems, and providing training on regulatory compliance. Additionally, we facilitated the certification process by coordinating with regulatory authorities and conducting pre-certification inspections. As a result, the client successfully obtained regulatory approval for their welded components and launched their products in the market on schedule.
Problem: A customer encountered weld quality issues in critical components used in high-pressure applications, sourced from multiple Turkish suppliers, leading to concerns about product reliability and safety.
- Solution: QCmatic conducted a comprehensive review of the welding procedures, materials, and inspection practices employed by each supplier, identifying inconsistencies and deficiencies in weld quality control. We developed standardized welding procedures and inspection protocols tailored to the specific requirements of high-pressure applications. Additionally, we provided hands-on training to welders and inspectors to ensure proper implementation of the new procedures. Through rigorous quality testing and validation, we verified the integrity and reliability of the welded components, providing the client with confidence in their product performance and safety.

Why Choose QCmatic for Third-Party Welding Engineering Services?
- Expertise: Our team of welding engineers has extensive experience and expertise in all aspects of welding engineering and quality assurance.
- Customized Solutions: We tailor our services to meet your specific welding requirements and project objectives, ensuring optimal results.
- Code Compliance: We ensure that all welding procedures and practices adhere to relevant industry codes, standards, and regulations.
- Collaborative Approach: We work closely with your team to understand your needs and objectives, fostering collaboration and communication throughout the project.
- Commitment to Quality: At QCmatic, we are committed to delivering excellence in welding engineering services and helping you achieve your welding goals.
Ensure Weld Quality with QCmatic’s Expert Visual Testing Services
At QCmatic, we understand the crucial role that welding quality plays in the integrity and performance of your products. Our Visual Testing (VT) services for welding provide a cost-effective and efficient method to ensure that your welding processes meet the highest standards of quality, safety, and reliability. Leveraging international standards and best practices, we deliver thorough visual inspections to identify and rectify potential defects early in the production process.
Importance of Visual Testing in Welding
Visual Testing is a fundamental non-destructive testing (NDT) method that involves examining welds for surface defects and overall quality. It is often the first step in the quality assurance process, providing immediate feedback on the welding process and ensuring that any visible defects are identified and addressed promptly. VT is crucial for preventing structural failures, ensuring safety, and maintaining product integrity.


International Standards for Visual Testing of Welding
QCmatic’s Visual Testing services adhere to recognized international standards to ensure comprehensive and reliable inspections. Some of the key standards we follow include:
- ISO 17637:2016 – Non-destructive testing of welds — Visual testing of fusion-welded joints
- This standard provides guidelines for visual inspection of welds to detect surface-breaking defects. It covers the necessary conditions for inspection, such as lighting and access, as well as the qualifications of the inspectors.
- AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2020 – Structural Welding Code – Steel
- This standard establishes the requirements for welding steel structures, including criteria for visual inspection. It provides detailed guidelines on weld sizes, profiles, and acceptable levels of imperfections.
- ASME Section V, Article 9 – Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code
- This section of the ASME code covers visual examination procedures for pressure vessels and boilers. It includes requirements for inspector qualifications, examination methods, and acceptance criteria for various types of welds.
- EN 970:1997 – Non-destructive examination of fusion welds — Visual examination
- This European standard specifies requirements for the visual examination of welds in metallic materials. It outlines the techniques for performing visual inspections, criteria for acceptance, and documentation requirements.
- ISO 5817:2014 – Welding — Fusion-welded joints in steel, nickel, titanium, and their alloys (beam welding excluded) — Quality levels for imperfections
- This standard defines quality levels for imperfections in fusion-welded joints for a variety of materials. It provides a classification system for weld imperfections and their permissible limits based on the intended use of the welded structure.
- ISO 3834-2:2005 – Quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials
- This standard specifies comprehensive quality requirements for fusion welding processes. It includes guidelines on inspection and testing, including visual examination, to ensure the consistent quality of welded products.
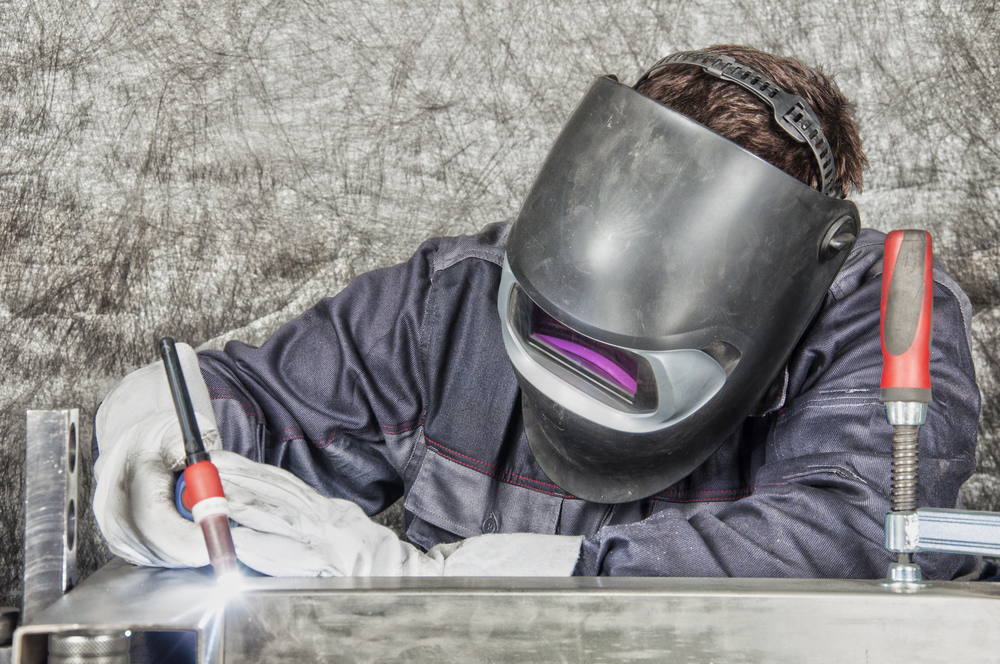
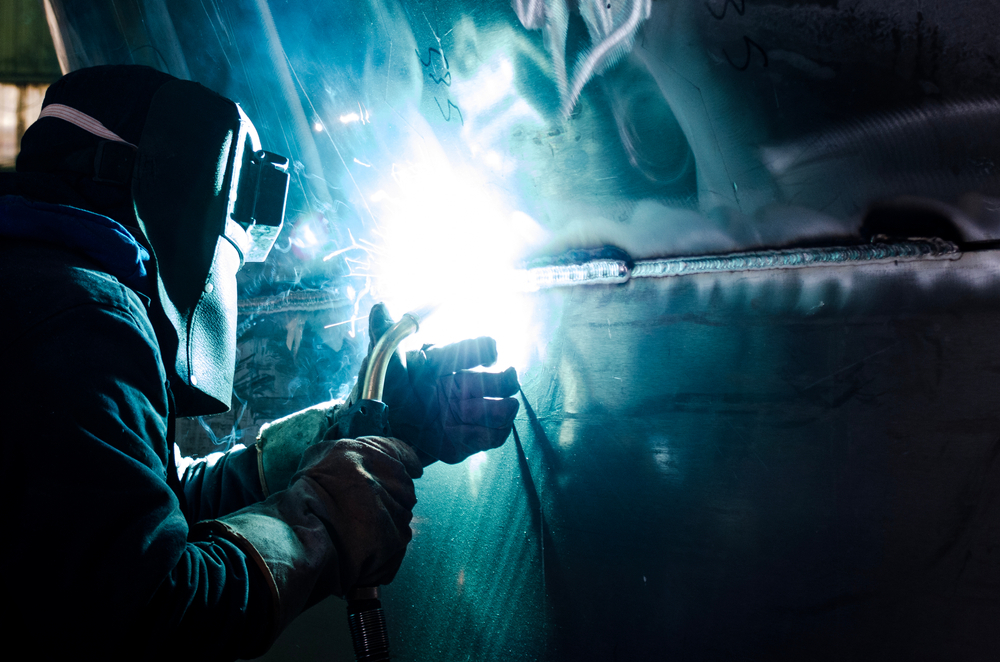



Visual Testing Methods
Our visual testing methods are designed to ensure thorough examination of welds, including:
- Direct Visual Inspection: This involves using the naked eye or magnifying tools to inspect welds for surface defects. Inspectors look for cracks, porosity, undercut, and misalignment. For example, in pipeline welding, inspectors might use magnifying glasses to closely examine the root pass of a weld to ensure there are no visible defects that could compromise the pipe’s integrity.
- Remote Visual Inspection: Utilizing borescopes, videoscopes, or other remote visual equipment to inspect areas that are difficult to access directly. This method is particularly useful for inspecting internal welds in complex assemblies such as pressure vessels or heat exchangers, where direct access is not possible.
- Optical Aids: Employing mirrors, magnifying glasses, and other optical aids to enhance the visibility of weld surfaces. For instance, during the inspection of structural welds on large construction projects, mirrors might be used to view the back side of a weld joint that is not directly accessible.
- Lighting Techniques: Proper lighting is critical for effective visual inspection. Techniques such as using angled lighting can help highlight surface defects. For example, angled lighting can make small surface cracks or undercuts more visible by casting shadows that reveal their presence.
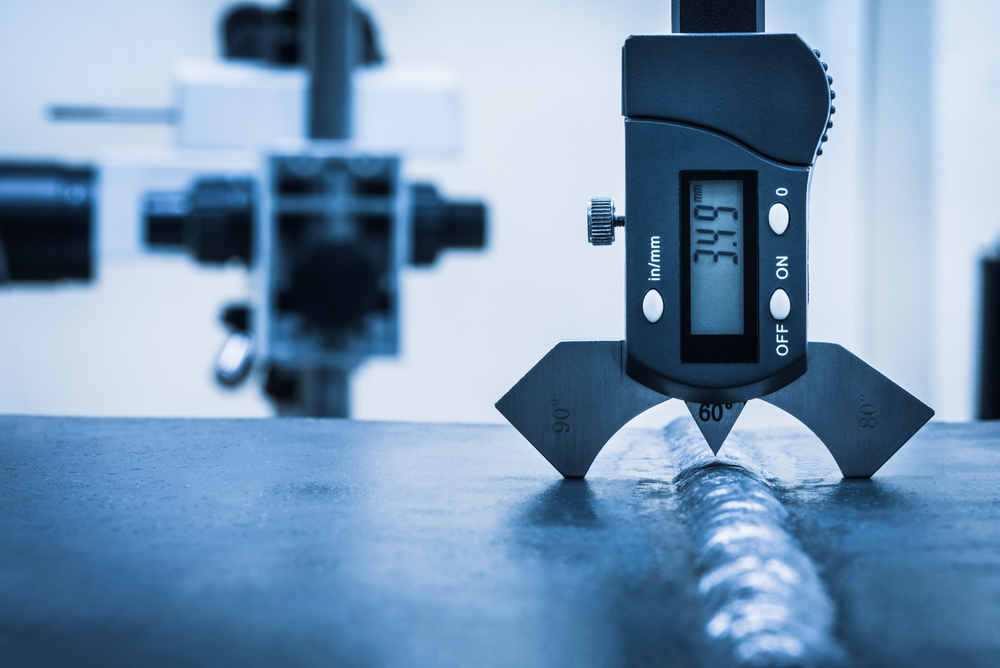
- Visual Gauges and Templates: Tools like weld gauges and templates are used to measure weld dimensions and ensure they meet specified criteria. For example, a fillet weld gauge can be used to check the leg length and throat thickness of a fillet weld to ensure it complies with design specifications.
- Surface Cleaning: Cleaning the weld surface before inspection to remove any contaminants that might obscure defects. This might involve wire brushing, grinding, or using solvents. For instance, in the automotive industry, welds on chassis components are often cleaned before inspection to ensure accurate assessment.
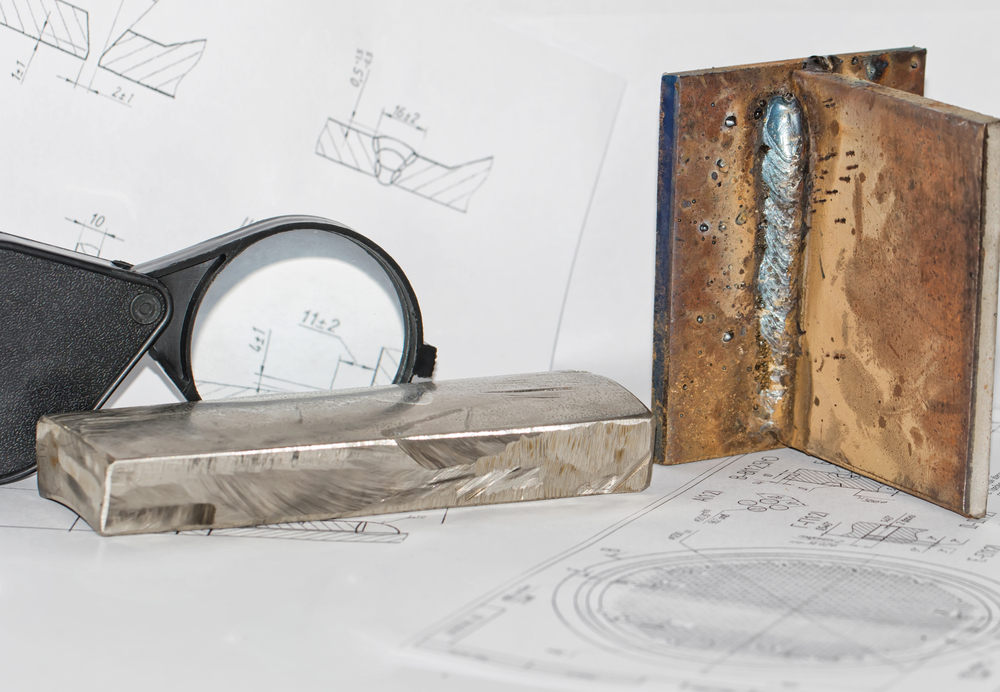
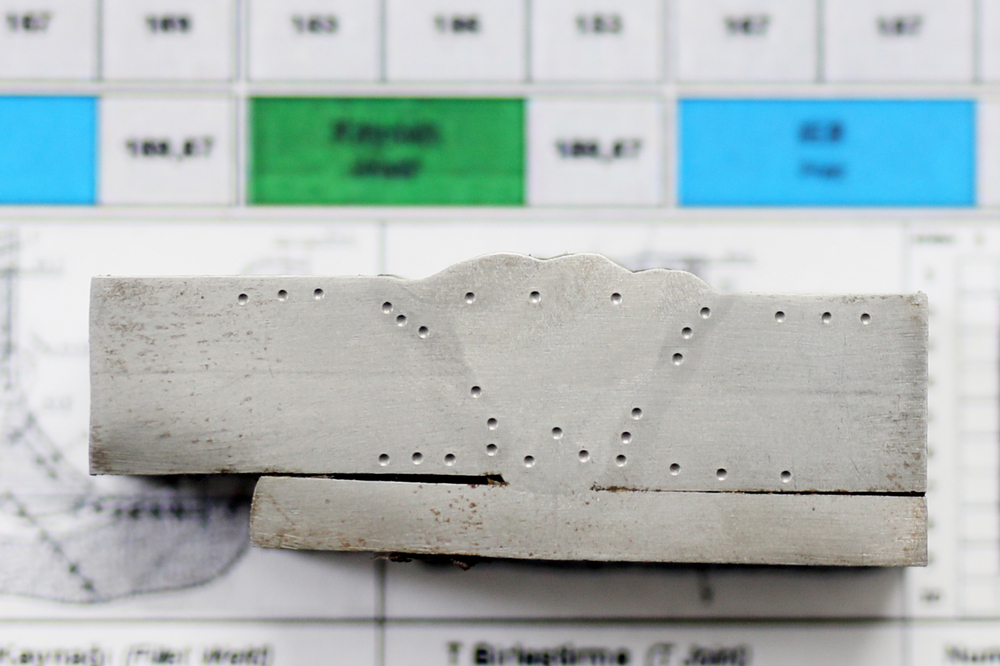
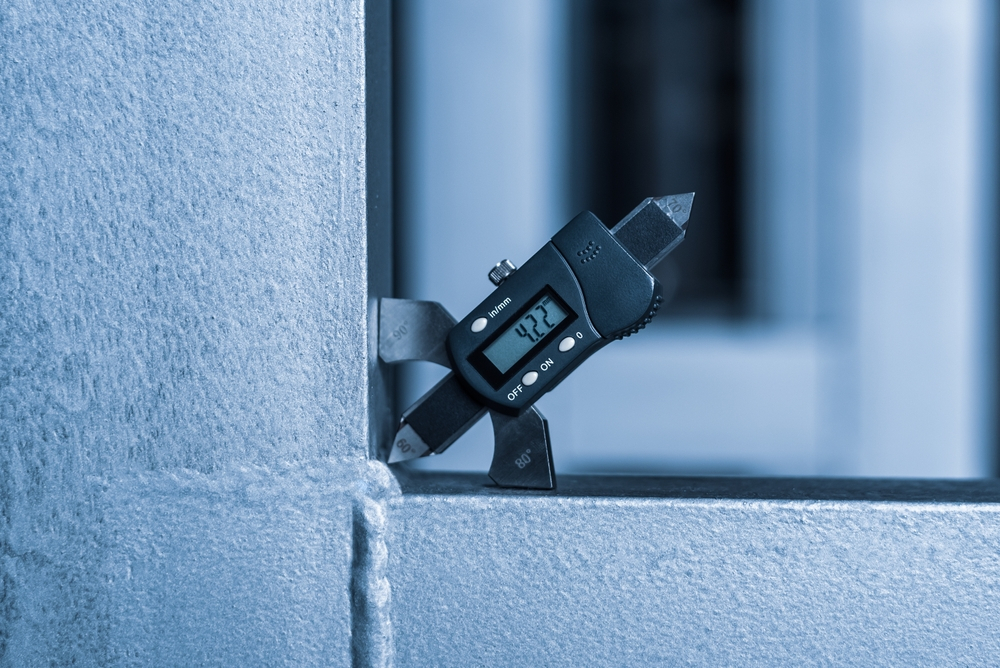



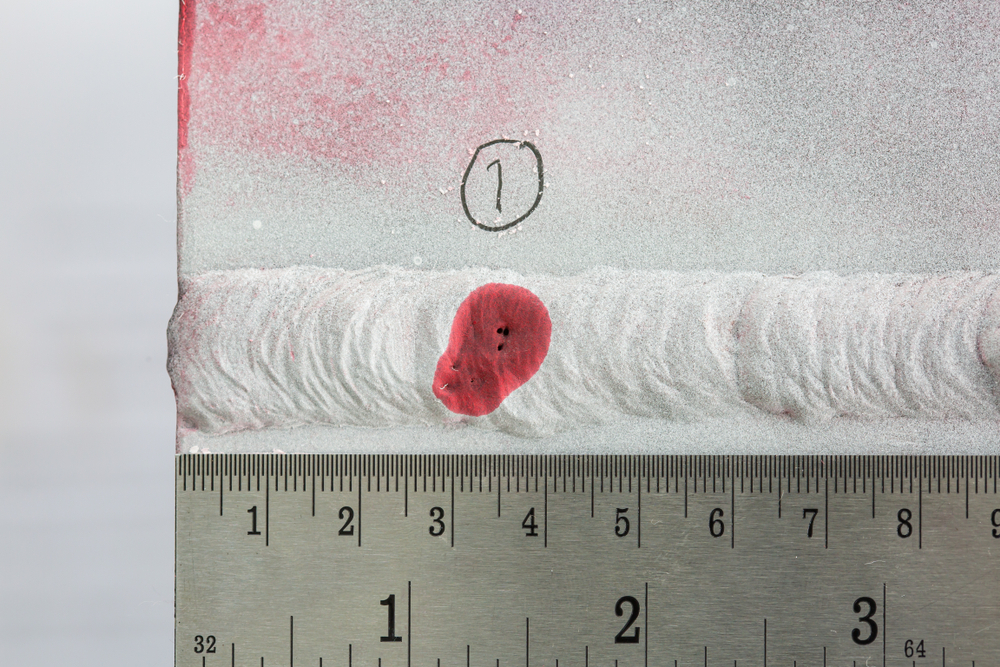
Examples of Visual Defects in Welding and Their Root Causes
During visual inspection, we look for common welding defects, identify their root causes, and suggest corrective actions. Here are some examples:
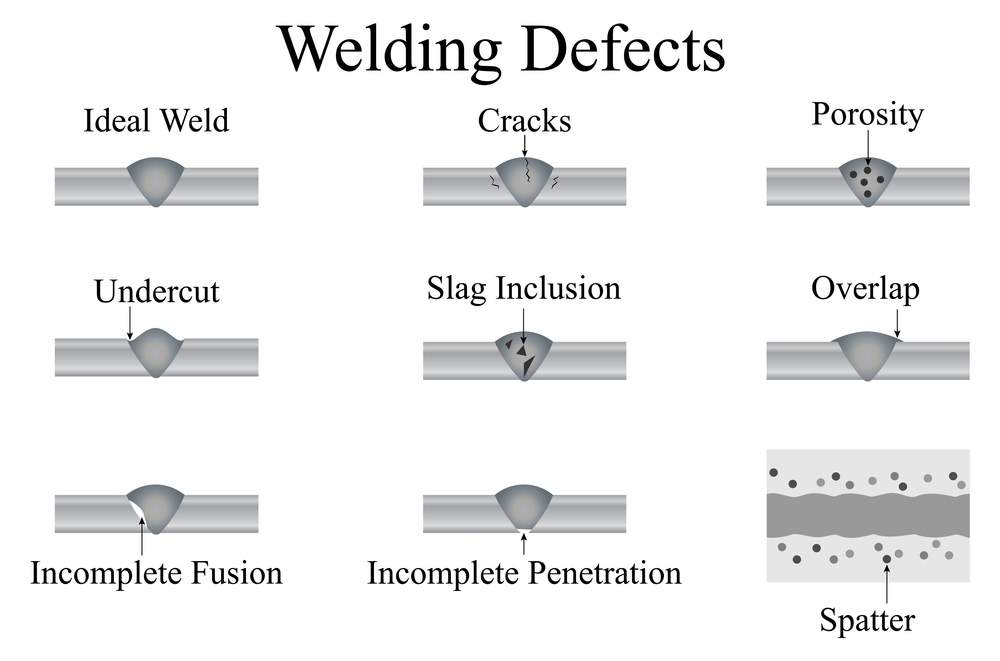
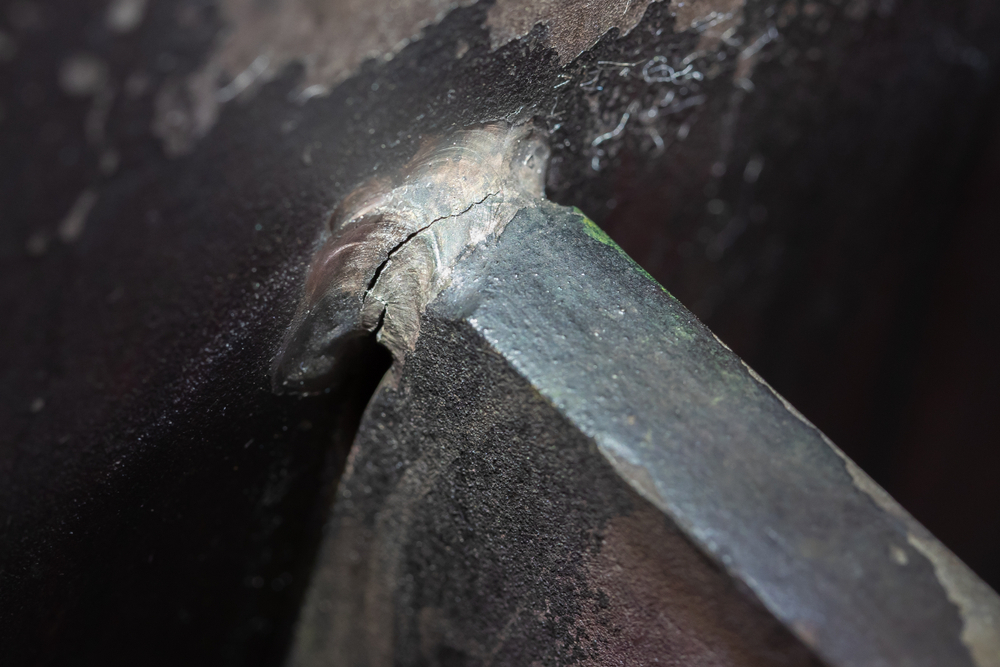
- Cracks
- Description: Linear discontinuities that can compromise the integrity of the weld.
- Root Causes: Rapid cooling, high residual stress, incorrect welding parameters, or poor joint design.
- Prevention: Proper preheat and post-weld heat treatment, appropriate welding techniques, and stress-relief processes.
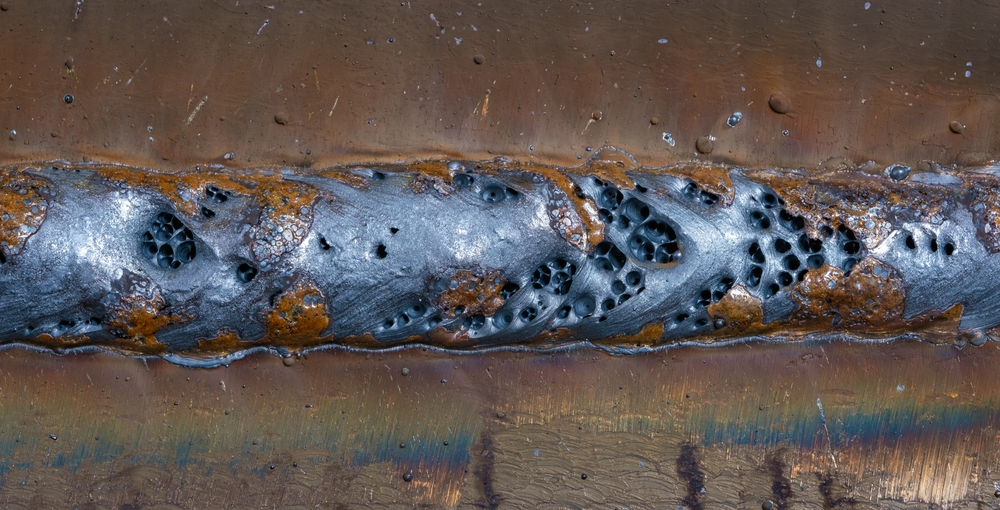
- Porosity
- Description: Small holes or voids in the weld caused by trapped gas.
- Root Causes: Contaminated base or filler material, improper shielding gas, excessive welding speed.
- Prevention: Clean materials and surfaces, correct gas flow rates, and controlled welding speed.
- Undercut
- Description: Grooves melted into the base material adjacent to the weld toe.
- Root Causes: Excessive welding current, incorrect electrode angle, too fast travel speed.
- Prevention: Use appropriate welding current and angle, control travel speed.
- Incomplete Fusion
- Description: Lack of proper fusion between the weld metal and base metal.
- Root Causes: Low heat input, improper joint preparation, incorrect welding technique.
- Prevention: Ensure adequate heat input, proper joint preparation, and use correct welding technique.
- Overlapping
- Description: Excess weld metal that extends beyond the weld toe without proper fusion.
- Root Causes: Excessive deposition rate, incorrect torch angle, insufficient heat.
- Prevention: Control deposition rate, maintain proper torch angle, ensure adequate heat input.
- Slag Inclusions
- Description: Non-metallic solid material trapped in the weld metal.
- Root Causes: Improper slag removal between passes, incorrect welding technique, contaminated materials.
- Prevention: Ensure thorough slag removal, use correct welding technique, and clean materials.
- Excessive Spatter
- Description: Small metal particles expelled during welding that adhere to the surface.
- Root Causes: High welding current, incorrect polarity, improper shielding gas.
- Prevention: Use appropriate welding current and polarity, adjust shielding gas flow.
- Burn-Through
- Description: A hole melted completely through the base metal.
- Root Causes: Excessive heat input, thin base material, incorrect welding technique.
- Prevention: Use proper heat input control, consider base material thickness, correct welding technique.
- Distortion
- Description: Warping or deformation of the welded components.
- Root Causes: Uneven heating and cooling, excessive welding heat input, improper clamping or fixturing.
- Prevention: Use proper heat control, preheat and post-weld heat treatment, proper clamping and fixturing.
- Weld Misalignment
- Description: Misalignment of the welded components.
- Root Causes: Poor fit-up, incorrect joint preparation, improper fixturing.
- Prevention: Ensure proper fit-up, accurate joint preparation, and adequate fixturing.
- Lack of Penetration
- Description: Incomplete penetration of the weld into the joint thickness.
- Root Causes: Low welding current, incorrect welding technique, improper joint preparation.
- Prevention: Increase welding current, improve joint preparation, and use appropriate welding technique.
- Root Concavity
- Description: Depression at the root of a weld bead.
- Root Causes: Low welding current, improper welding technique, insufficient filler material.
- Prevention: Increase welding current, improve welding technique, and ensure adequate filler material.
- Root Cracking
- Description: Cracks occurring at the root of the weld bead.
- Root Causes: High residual stress, improper joint design, inadequate preheat or post-weld heat treatment.
- Prevention: Apply proper preheat and post-weld heat treatment, use appropriate joint design, and control residual stress.
- Overlap
- Description: The weld metal rolls over the base metal without fusing to it.
- Root Causes: Excessive weld metal deposition, improper welding technique, low travel speed.
- Prevention: Control weld metal deposition rate, use proper welding technique, and maintain appropriate travel speed.
- Arc Strikes
- Description: Localized points of surface melting caused by accidental arc contact.
- Root Causes: Unintentional arc strikes during welding, improper electrode handling.
- Prevention: Avoid unintentional arc strikes, use proper electrode handling techniques.
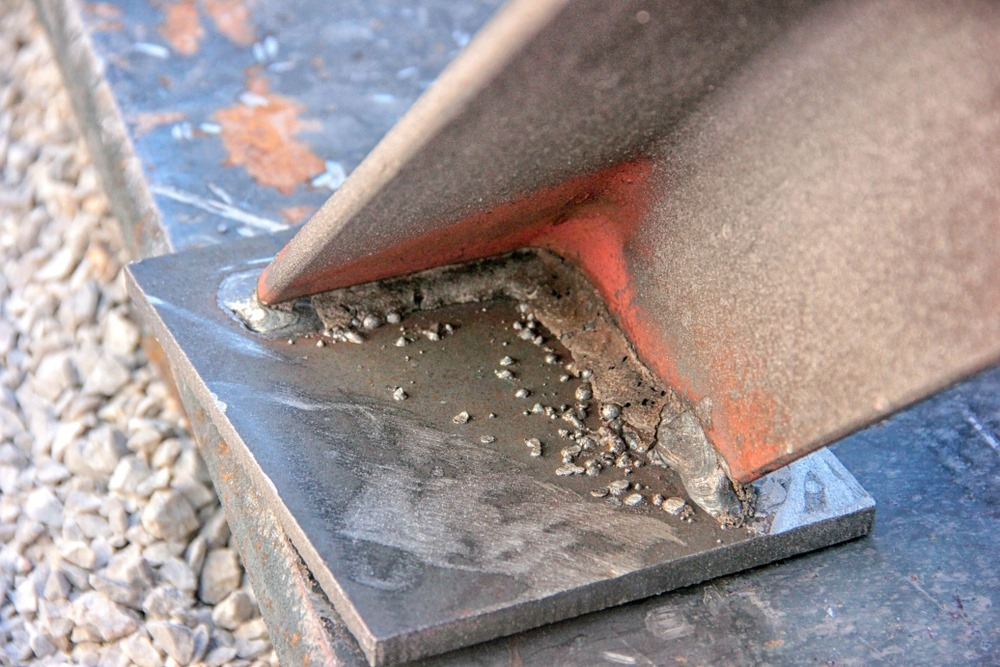
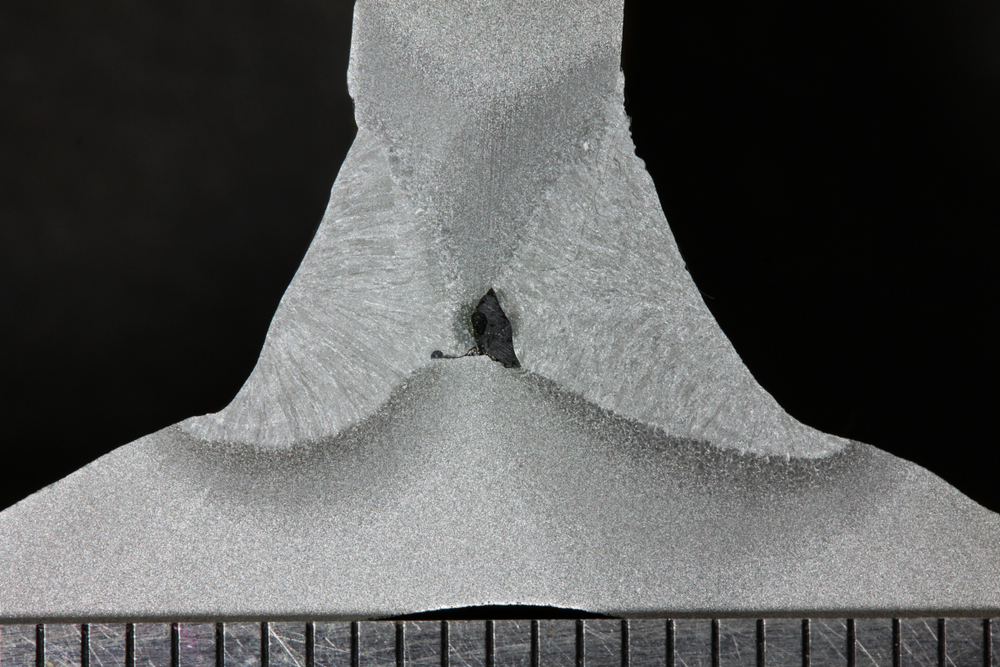







Documentation Control in Welding
Effective documentation control is essential for welding verification and validation. QCmatic ensures that all relevant documents are accurately maintained and readily available. Key documents include:
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR): A record of welding data used to confirm that the welding procedure specification (WPS) can produce welds meeting the required standards. The PQR includes details on materials, welding parameters, and test results.
- Related Standards: ASME Section IX, ISO 15614-1
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS): A document providing detailed welding instructions, including material types, welding processes, joint design, position, preheat and post-weld heat treatment, and necessary qualifications.
- Related Standards: ASME Section IX, ISO 15609-1
- Welder Qualification Test Record (WQTR): Documentation that verifies a welder’s ability to produce welds that meet the specified standards. This includes test results and certifications.
- Related Standards: ASME Section IX, ISO 9606-1
- Inspection and Test Plans (ITP): Plans outlining the inspection and testing activities to be performed during the welding process. This includes stages of inspection, methods to be used, and acceptance criteria.
- Related Standards: ISO 3834-2
- Material Test Reports (MTR): Reports that certify the materials used in welding meet specified standards. These include chemical composition and mechanical properties of the base and filler materials.
- Related Standards: EN 10204, ASTM A370
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Reports: Documentation of all NDT results, including visual, ultrasonic, radiographic, and other testing methods. These reports provide evidence of weld quality and integrity.
- Related Standards: ISO 17637, ISO 5817
- Weld Maps and Logs: Diagrams and records detailing the location, identification, and inspection status of each weld. This helps in tracking and verifying weld quality across the project.
- Related Standards: ISO 3834-5
- Quality Control Records: Comprehensive records of all quality control activities, including inspections, test results, and corrective actions. These records ensure traceability and compliance with quality standards.
- Related Standards: ISO 9001


Why Choose QCmatic for Visual Testing of Welding?
Our QMS and process audit services cater to a wide range of industries, including:
- Expertise: Our team of experienced inspectors is highly skilled in visual testing techniques and standards.
- Compliance: We adhere to international standards to ensure thorough and reliable inspections.
- Comprehensive Services: Our visual testing services cover all aspects of weld quality control.
- Detailed Documentation: We provide detailed documentation to support verification and validation processes.
- Commitment to Quality: At QCmatic, we are dedicated to helping you achieve the highest standards of welding quality and reliability.





Industries We Serve
Our QMS and process audit services cater to a wide range of industries, including:
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- General Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery
- Railways
- Medical Equipment Manufacturing
- Petrochemicals
- Construction Machinery
- Truck Mounted Equipment
- Energy
- Metalworking
- Manufacturing

